
B ^ ^ ^ The historical basis for designating the stop codons as amber, ochre and opal is described in an autobiography by Sydney Brenner and in a historical article by Bob Edgar. The other start codons listed by GenBank are rare in eukaryotes and generally codes for Met/fMet.
#Mrna start codon code
Standard genetic code Amino-acid biochemical propertiesĪ The codon AUG both codes for methionine and serves as an initiation site: the first AUG in an mRNA's coding region is where translation into protein begins. don't initiate translation or because ribosomes terminating after translation of short ORFs are often capable of reinitiating). However, it is believed that most translated uORFs only have a mild inhibitory effect on downstream translation because most uORF starts are leaky (i.e.
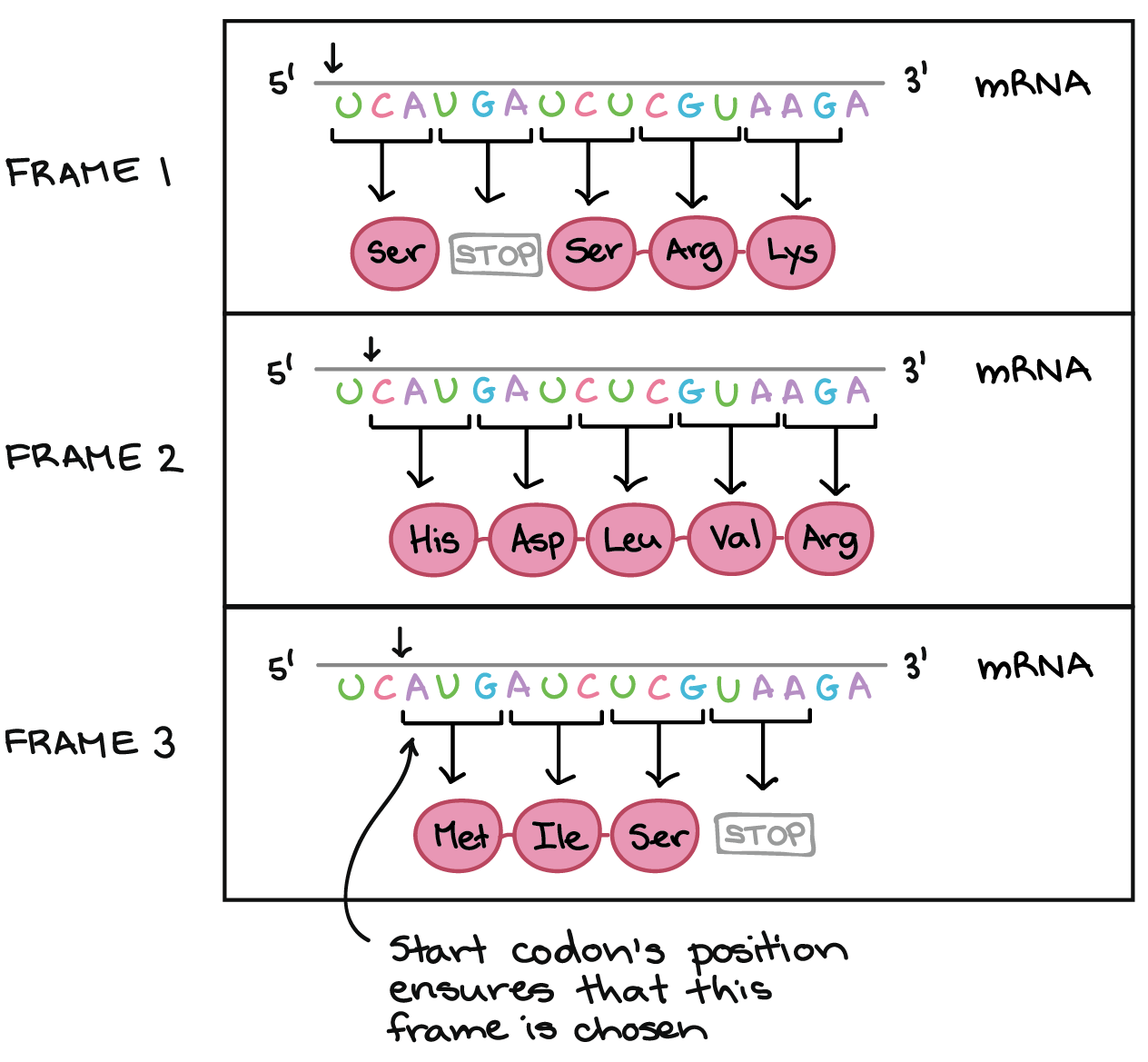
uORF translation usually results in the synthesis of short polypeptides, some of which have been shown to be functional, e.g., in ASNSD1, MIEF1, MKKS, and SLC35A4. Their potential use as TISs could result in translation of so-called upstream Open Reading Frames (uORFs). More than half of all human mRNAs have at least one AUG codon upstream (uAUG) of their annotated translation initiation starts (TIS) (58% in the current versions of the human RefSeq sequence). These are "alternative" start codons in the sense that they are upstream of the regular start codons and thus could be used as alternative start codons. Many such examples, with codons, systematic range, and citations, are given in the NCBI list of translation tables. Mitochondrial genomes use alternate start codons more significantly (AUA and AUG in humans). Two more recent studies have independently shown that 17 or more non-AUG start codons may initiate translation in E. Well-known coding regions that do not have AUG initiation codons are those of lacI (GUG) and lacA (UUG) in the E. Prokaryotes use alternate start codons significantly, mainly GUG and UUG.Į. In addition to the canonical Met-tRNA Met and AUG codon pathway, mammalian cells can initiate translation with leucine using a specific leucyl-tRNA that decodes the codon CUG. Seven out of the nine possible single-nucleotide substitutions at the AUG start codon of dihydrofolate reductase are functional as translation start sites in mammalian cells. However, naturally occurring non-AUG start codons have been reported for some cellular mRNAs. Eukaryotes Īlternate start codons (non-AUG) are very rare in eukaryotic genomes. This is because a separate transfer RNA (tRNA) is used for initiation. Alternate start codons are still translated as Met when they are at the start of a protein (even if the codon encodes a different amino acid otherwise). In prokaryotes this includes the ribosome binding site.Īlternative start codons are different from the standard AUG codon and are found in both prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotes. The start codon is often preceded by a 5' untranslated region ( 5' UTR). The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. In this genomic region, the two genes overlap. For each nucleotide triplet (square brackets), the corresponding amino acid is given (one-letter code), either in the +1 reading frame for MT-ATP8 (in red) or in the +3 frame for MT-ATP6 (in blue). First codon of a messenger RNA translated by a ribosome Start codon (blue circle) of the human mitochondrial DNA MT-ATP6 gene.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
